목차
- Problem definition
- Background
- Bandit with Maximum Tsallis Entropy
- Maximum Tsallis Entropy in MDPS
- Dynamic Programming for Tsallis MDPs
- Tsallis Actor Critic for Model-Free RL
- Experiment
- Reference
1. Problem definition
이전에 RL의 exploration을 더 잘하기 위해서 entropy 개념을 도입하여 최적화하였다. 그 대표적인 entropy가 Shannon-Gibbs(SG) entropy이다. 역설적으로 exploration을 더 잘하게 만들어서 exploit이 감소하여 performance가 감소하는 문제도 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해 entropy decaying과 같은 방법을 통해 해결하였다. 다른 방법으로는 sparse Tsallis(ST) entropy를 사용하는 방법이있다. ST entropy는 exploration을 더 적게하여 suboptimal policy를 찾을 수 있다는 문제가 있다. 그래서 해당 논문에서는 Tsallis MDP문제로 정의하여 다양한 entropy를 cover할 수 있도록 제안한다.
2. Background
Shannon-Gibbs entropy
\[S = - \overset{n}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} p_i \operatorname{log}p_i\]이 entropy를 maximize하는 의미는 \(p_i\)를 모든 state에 대해서 같은 확률로 만든다는 의미이다.
\[- \overset{n}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} p_i \operatorname{log}p_i \leq - \overset{n}{\underset{i=1}{\sum}} \frac{1}{n} \operatorname{log}{\frac{1}{n}}\]q-Exponential, q-Logarithm and Tsallis Entropy
\[\operatorname{exp_q}(x) \triangleq \begin{cases} \operatorname{exp}(x) &\text{if q = 1}\\ [1+(q-1)x]^{\frac{1}{q-1}}_+ &\text{if q} \neq \text{1}\end{cases}\] \[\operatorname{ln}_q(x) \triangleq \begin{cases} \operatorname{log}(x) &\text{if q = 1 and x > 0}\\ \frac{x^{q-1}-1}{q-1} &\text{if q} \neq \text{1 and x > 0}\end{cases}\]where \([x]_+ = \operatorname{max}(x,0)\) and q is a real number
위 공식은 q-exponential, q-logarithm 공식이다. \(\operatorname{ln}_q(x)\)는 x에대해 단조 증가함수이다. q가 1일 경우 log(x)가 되며 q가 2일 경우 선형 함수가 된다. 하지만 q>2일 경우 \(d\operatorname{ln}_q (x)/dx\)는 증가, q<2일 경우 \(d\operatorname{ln}_q (x)/dx\)는 감소 함수가 된다.
Tsallis entorpy는 \(\operatorname{ln}_q(x)\)로 표현할 수 있다.
\[S_q(P) \triangleq \underset{X \sim P}{E} [-\operatorname{ln}_q(P(X))]\]q가 1일 경우 SG entropy가 되고 q가 2일 경우 ST entropy가 된다. q가 무한대일 경우 entropy는 0이 된다. q>0일 경우 Tsallis entropy는 concave function이 된다.
Proposition 1
Concave 증명
Assume that X is a finite space. Let P is a probability distribution over X. if q>0, then, \(S_q(P)\) is concave with respect to P.
proof. \(f(x) = -x \operatorname{ln}_q(x)\)이라고 정의(x>0). 이를 두번 미분.
1번 미분
\(\frac{df(x)}{dx} = -\operatorname{ln}_q(x) -x\operatorname{ln}_q^{'}(x)\)
2번 미분
\(\frac{d^2f(x)}{dx^2} = -\operatorname{ln}_q^{'}(x) -\operatorname{ln}_q^{'}(x) -\operatorname{ln}_q^{''}(x) = -2 \frac{(q-1)x^{q-2}}{q-1} - x\frac{(q-1)(q-2)x^{q-3}}{q-1}\) \(= -2x^{q-2}-x(q-2)x^{q-3} = -qx^{q-2}\)
-q는 항상 음수이고 x의 지수함수는 항상 양수이기 때문에 2번 미분한 값은 항상 음수로 나온다. 이 결과를 이용하여 다음과 같은 특성이 만족하는 것을 보일 수 있다.
\(\lambda_1, \lambda_2 \geq 0\), \(\lambda_1+\lambda_2 =1\)일 경우 probability \(P_1, P_2\)에 대해서 아래의 식을 만족한다.(중간값 정리)
\(S_q(\lambda_1P_1 + \lambda_2P_2) = \underset{x}{\sum}-(\lambda_1P_1(x) + \lambda_2P_2(x))\operatorname{ln}_q(\lambda_1P_1(x)+\lambda_2P_2(x))\) \(\ge \underset{x}{\sum} -\lambda_1P_1(x)\operatorname{ln}_q(P_1(x)) - \lambda_2P_2(x) \operatorname{ln}_q(P_2(x))\) \(=\lambda_1S_q(P_1) + \lambda_2S_q(P_2)\)
*위 식의 부등식(>)은 논문 부등식(<) 반대로 되어있다. 내가 생각하였을 때 중간값 정리를 적용하면 논문과 다르게 부등식이 반대로 되어야한다고 생각된다. 또한 뒤쪽에서 위 식을 사용하는 부분에서는 부등식이 반대로 되어 있기 때문에 > 부등식을 사용하는 것이 맞다고 생각한다.
그러므로 \(S_q(P)\)는 P에 대해서 concave하다.
Proposition 2
Entropy가 최대가되는 P 값 증명
Assume that X is a finite space. Then, S_q(P) is maximized when P is a uniform distribution. i.e., P= 1|X| where |x| is the number of elements in X.
proof. KKT condition을 이용하여 optimization problem 해결
기본적으로 discrete uniform distribution일 때 entropy가 최대값을 가진다는 것을 알고 있다. 이 논문에서는 다시 한번 증명을 하고 있고 이 내용을 후반 부 증명에서 사용했다.
\[\underset{P \in \triangle}{\operatorname{max}} S_q(P)\]where, \(\triangle = \{P \mid P(x) \geq 0, \underset{x}{\sum} P(x) =1\}\) is a probability simplex.
KKT condition:
\(\forall x \in X, \frac{\partial(S_q(\pi)-\underset{x}{\sum}\lambda^*(x)P(x) - \mu^*(1-\underset{x}{\sum}P(X)))}{\partial P(x)} \bracevert_{P(x)=P^*(x)}\) \(= -\operatorname{ln}_q(P^*(x))-(P^*(x))^{q-1}-\lambda^*(x) + \mu^*\) \(=-q \operatorname{ln}_q(P^*(x)) -1 -\lambda^*(x) + \mu^* =0\)
\(\forall x \in X, 0 = 1 -\underset{x}{\sum}P^*(x), P^*(x) \geq 0\)
\(\forall x \in X, \lambda^*(x) \leq 0\)
\(\forall x \in X, \lambda^*(x)P^*(x) =0\)
where \(\lambda^*\) and \(\mu^*\) are the Lagrangian multipliers for constraints in \(\triangle\)
세부 증명 1.
\(\frac {\partial S_q(\pi)} {\partial P(x)} = \frac{P(x)^{q-1}-1}{q-1} + P(x) \frac{(q-1)P(x)^{q-2}}{q-1}\)
\(=\frac{P(x)^{q-1}-1}{q-1} + \frac{(q-1)P(x)^{q-1}}{q-1}\) \(=\frac{qP(x)^{q-1}-1}{q-1}\) \(=\frac{qP(x)^{q-1} -q -1 +q}{q-1}\) \(=q\operatorname{ln}_qP(x)-1\)
세부 증명 2. 첫번째 KKT condition을 이용하여 \(P^*(x)\)에 대해서 정리
\(P^*(x) \ge 0\)이므로 \(\lambda^*(x) =0\)이 된다.
\(-q\operatorname{ln}_q(P^*(x)) -1 + \mu^*=0\)
\(\operatorname{ln}_q(P^*(x)) = \frac{-1+\mu^*}{q}\)
\(\frac{P^*(x)^{q-1}-1}{q-1} = \frac{-1 + \mu^*}{q}\)
\(P^*(x)^{q-1}-1 = (q-1) \frac{-1 + \mu^*}{q}\)
\(P^*(x) = (1+(q-1)\frac{-1 + \mu^*}{q})^{\frac{1}{q-1}}=\operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{\mu^* -1}{q})\)
P는 \(\mu\)와 q에 의해서만 결정된다.(constant probability mass) x에 대한 함수가 아니므로 \(P^*(x)=1/\vert S \vert\) where \(S=\{x \mid P^*(x) \ge0\}\)이다.(P가 모든 확률에 대한 uniform이 아닌 일부 확률에 대해서만 동일한 확률을 가질 수 있다. 물론 \(P^*(x) \ge 0\)이라고 condition이 있으므로 이미 uniform이라고 해도 될 것같다.)
Optimal value는 \(S_q(P^*)=-\operatorname{ln}_q(1/ \vert S \vert)\)이다. \(-\operatorname{ln}_q(x)\)는 단조 증가함수이므로 \(\mid S \mid\)는 최대가 되어야한다. S=X일 때 S가 최대가 되므로 \(P^*(x) = 1/\vert X \vert\)이다.
3. Bandit with Maximum Tsallis Entropy
MDP에 적용하기 전에 간단한 예제인 multi-armed bandit(MAB) 문제에 적용을 한다. MAB 문제에서 정의한 특성들이 MDP 문제에도 적용을 할 수 있다.
\[\underset{\pi \in \triangle}{\operatorname {max}} [\underset{a \sim \pi}{E}[R] + \alpha S_q(\pi)]\]MAB의 Tsallis entropy maximization은 위 식으로 정의된다.
\[\pi_q^*(a) = \underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_q (r(a)/q- \psi(r/q))\]Tsallis entroy의 stochastic optimal policy는 위 식으로 정의된다. \(\psi\)는 q-potential function으로 q-expoential, q-logarithm과 같은 q가 변수로 사용되는 function이다.
\[\underset{a \sim \pi^*}{E}[R] + \alpha S^*_q(\pi)=(q-1) \underset{a}{\sum}\frac{r(a)}{q} \operatorname{exp}_q (\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi_q(\frac{r}{q})) + \psi_q (\frac{r}{q})\]\(\pi^*_q\)를 이용한 optimal value는 위 식으로 정의된다. q가 1일 경우 optimal policy는 softmax distribution이 된다. q가 2일 경우 ST entropy를 이용한 optimal policy가 된다. \(\pi^*_1\)과 다르게 \(\pi^*_2\)는 0 probability를 만들 수 있다.(\(r(a) < 2\psi_2(r/2) -2\)일 경우) q가 무한대일 경우 기본적인 MAB problem이 된다. q가 1,2, 무한대 일경우 \(\psi_q\)구하기 쉬웠지만 이외의 경우는 어렵다. 다른 논문에서 이를 first order tayler expansion으로 구하는 방법을 소개했지만 이 논문에서는 다른 방법을 사용한다.(section 6에서 다뤄진다. network를 이용하여 update하는 방법을 사용)
Proposition 3
Optimal solution of MAB with maximum Tsallis entropy
The optimal solution of
\[\underset{\pi \in \triangle}{\operatorname{max}} [ \underset{a \sim \pi}{E} [R] + S_q(\pi)]\]is
\[\pi^*_q(a) = \operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi_q(\frac{r}{q}))\]where the q-potential function \(\psi_q\) is a functional define on {A,r}
\(\psi\)는 아래의 공식의 condition에 의해서 결정된다.
\[\underset{a}{\sum}\pi^*_q(a) = \underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_q (\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi (\frac{r}{q})) =1\]\(\psi^*_q\)를 이용해서 optimal value는 아래와 같이 정의할 수 있다.
\[\underset{\pi \in \triangle}{\operatorname{max}} [ \underset{a \sim \pi}{E} [R] + S_q(\pi)] = (q-1) \underset{a}{\sum} \frac{r(a)}{q} \operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi_q \frac{r}{q}) + \psi_q(\frac{r}{q})\]proof. \(\operatorname{exp}_q \in [0, \infty)\)는 continous 단조 함수 이기 때문에 \(\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{r}{q} - \xi)\)는 0으로 수렴하고 \(\xi\)가 +,- 무한대일 경우 무한대로 수렴한다. 그러므로 \(\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{r}{q} - \xi^*)=1\)을 만족하는 \(\xi^*\)가 존재한다. 그러므로 \(\psi_q(r/q) = \xi^*\)라고 할 수 있다.
나머지는 KKT condition을 고려하여 구한다. KKT conditon:
\(\forall i, 1-\underset{a}{\sum} \pi^*_q(a) = 0, \pi^*_q(a) \geq 0\)
\(\forall i, \lambda^*(a) \leq 0\)
\(\forall i, \lambda^*(a)\pi^* =0\)
\(\forall i, r(a)-\mu^* - \operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) - (\pi^*_q(a))^{q-1}+\lambda^*(a)=0\)
마지막 condition은 아래 식으로부터 나온다. \(\frac{\partial}{\partial \pi}(\underset{a \sim \pi}{E}[R] + S_q(\pi) + \mu^*(1-\underset{a}{\sum} \pi(a))+\lambda^*(a)\pi(a))\)
마지막 condition은 아래와 같이 변환이 가능하다. \(0=r(a) -\mu^* - \operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) - (\pi^*_q(a))^{q-1} + \lambda^*(a)\)
\(0=r(a) -\mu^* - \operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) - (q-1)\frac{(\pi^*_q(a))^{q-1}}{q-1} + \lambda^*(a)\)
\(0=r(a) -\mu^* - \operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) - (q-1)\frac{(\pi^*_q(a))^{q-1}+1-1}{q-1} + \lambda^*(a)\)
\(0=r(a) -\mu^* - \operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) - (q-1)\frac{(\pi^*_q(a))^{q-1}-1}{q-1} -1 + \lambda^*(a)\)
\(0=r(a) -\mu^* - \operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) - (q-1)\operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*(a)) -1 + \lambda^*(a)\)
\(0=r(a) -\mu^* - q\operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) -1 + \lambda^*(a)\)
\(\pi^*_q(a) \ge 0\)이므로 \(\lambda^*(a) =0\)이 된다. 그러므로 위 공식은 아래와 같이 표현된다.
\(0=r(a) -\mu^* - q\operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a)) -1\)
\(q\operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a))=r(a) -\mu^* -1\)
\(\operatorname{ln}_q(\pi^*_q(a))=\frac{r(a)}{q} -\frac{\mu^* +1}{q}\)
\(\pi^*_q(a) = \operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{r(a)}{q} - \frac{\mu^*+1}{q})\)
이제 \(\mu^*\)를 구해야한다. 이 값은 \(\underset{a}{\sum}\pi^*_q(a)\)를 이용해 구할 수 있다. \(\underset{a}{\sum}\pi^*_q(a) = \underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_q (\frac{r(a)}{q} - \frac{\mu^*+1}{q})=1\)
이전에 \(\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_q (\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi_q (\frac{r}{q}))=1\)로 표현하였다. 위 두 식이 동일하다고 하면
\[\psi(\frac{r}{q}) = \frac{\mu^*+1}{q}\]이 된다. 이 식은 \(\mu^*\)에 대해서 풀면 해당 값을 얻을 수 있다.
\[\mu^* = q\psi_q(\frac{r}{q})-1\]\(\pi^*_q(a) \ge 0\)를 만족해야한다.(KKT condition)
\[1+(q-1)(\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi(\frac{r}{q})) \ge 0\]이므로 \(\pi^*_q(a) \ge 0\)를 만족한다.(위 식은 \(\pi^*_q(a)\)의 definition에 의한 식이다.)
- \(\mu^*\)가 이전 공식에서 비교해서 가져오는 것이 아닌 논문 저자의 수식 표현으로 정의할 때어디서 이 표현 수식의 idea를 가져왔는 지 과정이 궁금하다.
Optimal value problem은 아래의 수식으로 표현 가능하다.
\(\underset{a \sim \pi^*_q}{E}[R] + S_q(\pi^*_q)\)
\(=\underset{a}{\sum}r(a)\pi^*_q(a) - \underset{a}{\sum}[\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi(\frac{r}{q})]\pi^*_q(a)\)
\(=\underset{a}{\sum}[r(a)\pi^*_q(a) - \frac{r(a)}{q}\pi^*_q(a) + \underset{a}{\sum}\psi_q(\frac{r}{q})\pi^*_q(a)]\)
\(=\underset{a}{\sum} \frac{qr(a)-r(a)}{q} \pi^*_q(a) + \psi_q(\frac{r}{q})\underset{a}{\sum}\pi^*_q(a)\)
\(=(q-1)\underset{a}{\sum}\frac{r(a)}{q}\pi^*_q(a) + \psi_q(\frac{r}{q})\)
\(=(q-1)\underset{a}{\sum}\frac{r(a)}{q}\operatorname{exp}_q(\frac{r(a)}{q} - \psi_q(\frac{r}{q})) + \psi_q(\frac{r}{q})\)
Proposition 4
q에 따른 policy, q-potential 값 구하기
When q=1 and q=2, \(\psi_1, \pi^*_1\) and \(\psi_2, \pi^*_2\)의 연산 결과는 아래와 같다.
\[\pi^*_1 = \operatorname{exp}(r(a)-\psi_1(r))\] \[\psi_1(r) = \operatorname{log}\underset{a}{\sum}\operatorname{exp}(r(a))\] \[\pi^*_2 = [1+ (\frac{r(a)}{2} - \psi_2(\frac{r}{2}))]_+\] \[\psi_1(\frac{r}{2}) = 1+ \frac{\underset{a \in S}{\sum}r(a)/2 -1}{\vert S \vert}\]proof.
이전 공식 \(\pi^*_q(a) = \underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}(\frac{r(a)}{q} - \frac{\mu^*+1}{q})\)를 이용
q=1일 경우
\(\pi^*_1\)는 \(\operatorname{exp}(r(a) -\psi_1(r))\)이 된다.(이전의 \(\pi^*_q\)의 공식을 이용)
\[\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}(r(a) - \mu^*-1)=1\] \[\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}(r(a)) \operatorname{exp}(- \mu^*-1)=1\] \[\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}(r(a)) = \operatorname{exp}(\mu^*+1)\] \[\operatorname{log}(\underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}(r(a))) = \mu^* +1\]\(\mu^* +1 = \psi_1(r(a))\)이므로
\[\psi_1(r) = \operatorname{log} \underset{a}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}(r(a))\]q=2일 경우
\(\pi^*_2\)는 \(\operatorname{exp}(\frac{r(a)}{2} -\psi_2(\frac{r}{2}))\)이 된다.
\[\underset{a \in S}{\sum} \operatorname{exp}_2(\frac{r(a)}{2} - \frac{\mu^*+1}{2}) = \underset{a \in S}{\sum}(1+\frac{r(a)}{2} - \frac{\mu^*+1}{2})=1\] \[\underset{a \in S}{\sum} (1 + \frac{r(a)}{2}) = \underset{a \in S}{\sum} (\frac{\mu^*+1}{2}) +1\] \[\underset{a \in S}{\sum} (1 + \frac{r(a)}{2}) -1 = \vert S \vert (\frac{\mu^*+1}{2})\] \[\frac{\underset{a \in S}{\sum} (1 + \frac{r(a)}{2})-1}{\vert S \vert} = \frac{\mu^* +1}{2}\] \[\frac{\vert S \vert + \underset{a \in S}{\sum} (\frac{r(a)}{2})-1}{\vert S \vert} = \frac{\mu^* +1}{2}\]\(\frac{\mu^* +1}{2} = \psi_2(\frac{r}{2})\)이므로
\[\psi_2(\frac{r}{2})=1+ \frac{\underset{a \in S}{\sum}r(a)/2 -1}{\vert S \vert}\]q-Maximum
MAB문제에서 MDP문제로 확장하기 전에 q-maximum에 대해서 정의를 한다. q-mximum은 maximum operator의 bounded approximation으로 아래와 같이 정의된다.
\[\underset{x}{\text{q-max}}(f(x)) \triangleq \underset{P \in \triangle}{\text{max}} [\underset{X \sim P} {E} [f(X)] + S-q(P)]\]q-maximum operator는 아래와 같은 boundary를 가진다.
\[\underset{x}{\text{q-max}} (f(x)) + \text{ln}_q(1/{\vert X \vert}) \leq \underset{x}{\text{max}} (f(x)) \leq \underset{x}{\text{q-max}} (f(x))\]이 식은 maximum Tsallis entropy의 MDP performance bound를 분석할 때 사용할 수 있으며 Tsallis MDP의 optimality의 조건으로 사용할 수 있다.
Theorem 1
q-maximum bounds 증명
proof 1. lower bound
\(\underset{x}{\text{q-max}} (f(x)) = \underset{P \in \triangle}{\text{max}} [\underset{X \sim P}{E}[f(X)] + S_q(P)] \leq \underset{P \in \triangle}{\text{max}} \underset{X \sim P}{E}[f(X)] + \underset{P \in \triangle}{\text{max}} S_q(P)\)
\(= \underset{x}{\text{max}}(f(x)) - \text{ln}_q(\frac{1}{\vert X \vert})\)
proof 2. upper bound
P’이 한 값만 뽑을 수 있게 되어 있다면(P’(x) =1 when \(x=\text{argmax}_{x'}f(x')\), others P(x’)=0) P’의 Tsallis entropy는 0이 될 것이다.
\[\underset{x}{\text{q-max}}(f(x)) = \underset{P \in \triangle}{\text{max}} [\underset{X \sim P}{E}[f(X)] + S_q(P)] \geq \underset{X \sim P'}{E} [f(x)] + S_q(P') = f(\underset{x'}{\text{argmax}}f(x')) = \underset{x}{\text{max}}f(x)\] \[\underset{x}{\text{q-max}}(f(x)) \geq \underset{x}{\text{max}}f(x)\]4. Maximum Tsallis Entropy in MDPs
이젠 MAB가 아닌 Tsallis entropy를 최대화하는 MDP를 정의한다. Tsaalis entropy는
\[S^\infty_q (\pi) \triangleq E_{\tau \sim P, \pi}[\sum^\infty_{t=0} \gamma^t S_q(\pi(\cdot | s_t))]\]로 정의된다. 이를 원래 MDP의 최대화 공식에 넣으면 아래와 같이된다.
\[\underset{\pi \in \Pi}{\text{maximize}} [\sum^\infty_t \gamma^t R_t] + \alpha S^\infty_q(\pi)\]이 식을 통하여 state value와 state action value function은 아래와 같이 정의된다.
\[V^\pi_q(s) \triangleq E_{\tau \sim P, \pi} [\sum^\infty_{t=0} \gamma^t (R_t + \alpha S_q(\pi(\cdot|s_t)))|s_0=s]\] \[Q^\pi_q(s,a) \triangleq E_{\tau \sim P, \pi} [R_0 + \gamma V^\pi_q(s_1) |s_0=s, a_0=a]\]Tsallis MDP의 목적은 optimal policy distribution을 찾는 것이다. 우선 \(\pi\)를 \(\rho\)로 표현할 것이며 이 식이 \(\rho\)에 대해서 concave한 것을 보여줄 것이다. 마지막으로 error bound의 크기를 정의할 것이다.
Proposition 5,6 and lemma 9.1
TBE 증명하기 전 proposition 5,6, lemma 9.1
Theorem 9를 증명하기 전 2가지 proposition과 한 개의 lemma를 먼저 얘기하고자한다. 이 식들은 \(\pi\)를 state action visitation인 \(\rho\)로 변환하는 데 사용된다.
- Proposition 5.
위 두식을 만족한다면 식을 만족한다.
\[\rho_\pi(s) = \sum_a \rho_\pi(s,a)\] \[\rho_\pi(s,a) = \rho_\pi(s) \pi(a|s)\] \[\sum_a\rho_\pi(s,a) = d(s) + \sum_{s',a'} P(s|s',a') \rho_\pi(s',a')\]- Proposition 6.
만약 \(\rho \in M\)이라면 state action visitation을 이용해 \(\pi_\rho(a|s) \triangleq \frac{\rho(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s,a')}\) 로 표현할 수 있고 \(\pi_\rho\)는 state-action visitation이 \(\rho\)인 유일한 policy이다.
- Lemma 9.1
위 두 Proposition 5,6을 통하여 policy와 state action visitation이 1:1 대응이 된다는 것을 알 수 있었다. 이 lemma에서는 \(\pi\)를 \(\rho\)로 변환할 것이다.
\[\bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho) = - \sum_{s,a} \rho(s,a) \text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s,a')})\]위 식을 만족한다면 \(\pi \in \Pi\)의 어떤 stationary policy와 \(\rho \in M\)의 어떤 state-action visitation measure에 대해서 \(S^\infty_q(\pi) = \bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho_\pi)\)를 만족한다.
Proof.
\[S^\infty_q(\pi) = E_{\tau \sim P, \pi}[\sum^\infty_{t=0} \gamma^t S_q(\pi(\cdot|s_t))] = \sum_s S_q(\pi(\cdot|s)) \cdot E_{\tau \sim P, \pi} [\sum^\infty_{t=0} \gamma^t 1(s_t=s)]\] \[= \sum_s S_q(\pi(\cdot | s)) \rho_\pi(s) = \sum_{s,a} - \text{ln}_q(\pi(a|s)) \pi(a|s) \rho_\pi(s)\] \[= \sum_{s,a} -\text{ln}_q(\pi(a|s)) \frac{\rho(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s,a')} \sum_{a'} \rho(s,a')\] \[=\sum_{s,a} - \text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho_\pi(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_\pi(s,a')})\rho_\pi(s,a)=\bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho_\pi)\]- Corollary 9.1.1
\(\rho\)가 optimal이면 \(\pi\)가 optimal인 것을 설명
\[J(\pi') + S^\infty_q(\pi') > J(\pi_{\rho^*}) + S^\infty_q(\pi_{\rho^*})\]where, \(J(\pi) = E_{\tau \sim \pi, P} [\sum^\infty_{t=0} \gamma^t R_t]\)
위 식은 아래 식으로 변경이 가능하다.
\[\sum_{s,a} \rho_{\pi'}(s,a) r(s,a) + \bar{s}^\infty_q(\rho_{\pi'}) > \sum_{s,a} \rho^*(s,a) r(s,a) + \bar{s}^\infty_q(\rho^*)\]하지만 \(\rho^*\)는 optimal이기 때문에 모순이다.
\[J(\pi') + S^\infty_q(\pi') \leq J(\pi_{\rho^*}) + S^\infty_q(\pi_{\rho^*})\]위 식이 맞는 식이 되고 \(\rho^*\)가 optimal이면 \(\pi^*\)도 optimal이 된다.
Lemma 9.2
Variable Change
subject to \(\forall s, a, \rho(s,a) \geq 0, \sum_a \rho(s,a) = d(s) + \sum_{s',a'} P(s |s',a') \rho(s',a')\)
이전의 Proposition 6과 Lemma 9.1을 통하여 Tsallis MDP를 \(\pi\) 대신 \(\rho\)로 표현이 가능하다. 그리고 이 ㅅ식을 이용해서 convcave한 것을 증명할 것이다.
Lemma 9.2 \(\bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho)\) is concave function with respect to \(\rho \in M\)
Proof.
\(f(x) = -x\text{ln}_q(x)\)라고 할 때 2차 미분 값은 \(-qx^{q-2}\)가 되고 이 값은 x가 0보다 클 때 음수가 된다. 즉 f(x)는concave function이라고 할 수 있다. concave function은 다른 방법으로 아래 식과 같은 중간값 정리를 이용하여 증명할 수 있다.
\[\bar{S}^\infty_q(\lambda_q \rho_1 + \lambda_2 \rho_2) > \lambda_1 \bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho_1) + \lambda_2 \bar{S}^\infty_q (\rho_2)\]where, \(0<\lambda_1, \lambda_2 < 1\), \(\lambda_1 + \lambda_2 =1\), \(\rho_1, \rho_2 \in M\)
\(\widetilde{\rho}\)를 \(\lambda_1 \rho_1 + \lambda_2 \rho_2\)라고 정의하고 \(\mu_1 = \frac{\lambda_1 \sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')}\) 그리고 \(\mu_2 = \frac{\lambda_2 \sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')}\) 라고 정의한다. 그리고 \(\mu_1 + \mu_2 =1\)이 된다.
\[\bar{S}^\infty_q(\lambda_1 \rho_1 + \lambda_2 \rho_2) = -\sum_{s,a} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\lambda_1 \rho_1 (s,a) + \lambda_2 \rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')})\] \[= -\sum_{s,a} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\lambda_1 \rho_1 (s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')}+ \frac{\lambda_2 \rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')})\] \[= \sum_{s,a} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\lambda_1 \frac{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1 (s,a')} \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')} + \lambda_2 \frac{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2 (s,a')} \frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')} )\] \[= - \sum_{s,a} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\mu_1 \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')} + \mu_2 \frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')})\] \[= - \sum_{s,a} \frac{\sum_{a'}\widetilde{\rho}(s,a')}{\sum_{a'}\widetilde{\rho}(s,a')}(\lambda_1 \rho_1(s,a)+\lambda_2 \rho_2(s,a)) \text{ln}_q (\mu_1 \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')} + \mu_2 \frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')})\] \[= - \sum_{s,a} \sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a') (\frac{\mu_1 \rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')} + \frac{\mu_2 \rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')}) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\mu_1 \rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1 (s,a')} + \frac{\mu_2 \rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2 (s,a')})\]그러므로 아래 식을 만족한다.
\(- (\frac{\mu_1 \rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')} + \frac{\mu_2 \rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')}) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\mu_1 \rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1 (s,a')} + \frac{\mu_2 \rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2 (s,a')})\) \(> - \mu_1 \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho_1(s,a')} \text{ln}_q (\frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')}) - \mu_2 \frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho_2(s,a')} \text{ln}_q (\frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')})\)
\(\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a') \mu_1 \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')}= \sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a') \frac{\lambda_1 \sum_{a'} \rho_1 (s,a')}{\sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a')} \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')} = \lambda_1\rho_1(s,a)\)이므로 우리는 위 식을 정리하면 아래를 얻을 수 있다.
\[\bar{S}^\infty_q (\lambda_1 \rho_1 + \lambda_2 \rho_2) > - \sum_{s,a} \sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a') \mu_1 \frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho_1(s,a')} \text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')})\] \[\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad- \sum_{s,a} \sum_{a'} \widetilde{\rho}(s,a') \mu_2 \frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho_2(s,a')} \text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_2(s,a')})\] \[= - \sum_{s,a} \lambda_1 \rho_1(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\rho_1(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho_1(s,a')}) - \sum_{s,a} \lambda_2 \rho_2(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\rho_2(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho_2(s,a')})\] \[= \lambda_1 \bar{S}^\infty_q (\rho_1) + \lambda_2 \bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho_2)\]위 식을 통해 concave함을 증명하였다. (q가 0보다 클 경우)
- Corollary 9.2.1
subject to \(\forall s, a, \rho(s,a) \geq 0, \sum_a \rho(s,a) = d(s) + \sum_{s',a'} P(s |s',a') \rho(s',a')\)
이 식은 첫 번째 term은 linear하고 두 번째 term은 concave하니 concave problem이라고 할 수 있다.
Tsallis Bellman Optimality Equation
q-maximum operator를 이용하여 Tsallis MDP의 optimality condition은 아래와 같이 정의할 수 있다.
\[Q^*_q(s,a) = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma V^*_q(s') |s,a]\] \[V^*_q(s) = \underset{a}{\text{q-max}} (Q^*_q(s,a))\] \[\pi^*_q(a|s) = \text{exp}_q (Q^*_q(s,a)/q - \psi_q(Q^*_q(s,\cdot)/q))\]where, \(\psi_q\) is a q-potential function.
위 식을 얻기 위해서 이전과 다르게 KKT condition을 이용해서 구했다.
Theorem 9
Proof of Tsallis Bellman Optimality Equation
\(L \triangleq \sum_{s,a} \rho(s,a) r(s,a) - \sum_{s,a} \rho(s,a) \text{ln}_q (\frac{\rho(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s,a')}) + \sum_{s,a} \lambda (s,a) \rho(s,a)\) \(+ \sum_s \mu(s) (d(s) + \sum_{s',a'} P(s|s',a') \rho(s',a') + \sum_a \rho(s,a))\)
where \(\lambda(s,a)\) and \(\mu(s)\) are dual variables for nonnegativity and Bellman flow constraints.
KKT condition:
\[\forall s, a, \rho^*(s,a) \geq 0, d(s) + \sum_{s',a'}P(s|s',a') \rho^*(s'a') - \sum_a \rho^*(s,a) =0\] \[\forall s, a, \lambda^*(s,a) \leq 0\] \[\forall s,a, \lambda^*(s,a) \rho^*(s,a) =0\] \[\forall s,a, 0 = \sum_{s'}r(s,a,s')P(s'|s,a) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') P(s'|s,a) - \mu^*(s)\] \[- q\text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho^*(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho^*(s,a')})-1 + \sum_a (\frac{\rho^*(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho^*(s,a')}) + \lambda^*(s,a)\]Lagrangian objective에서 \(\bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho)\)의 derivation된 kkt condition 값은 아래와 같이 유도된다.
\(\frac{\partial \bar{S}^\infty_q(\rho)}{\partial \rho(s'',a'')} = -\sum_{s,a} \frac{\partial \rho(s,a)}{\partial \rho(s'',a'')} \text{ln}_q (\frac{\rho(s,a)}{\sum_{a'} \rho(s,a')})\) \(- \sum_{s,a} \rho(s,a) \frac{\partial \text{ln}_q(\rho(s,a)/\sum_{a'} \rho(s,a'))}{\partial \rho(s'',a'')} -1\)
\(= -\text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho(s'',a'')}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s''a,')})\) \(- \sum_a \rho(s'',a)(\frac{\rho(s'',a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')})^{q-2}(\frac{\delta_{a''}(a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')} - \frac{\rho(s'',a)}{(\sum_{a'} \rho(s'',a'))^2})\)
\[= -\text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho(s'',a'')}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')}) - (\frac{\rho(s'',a'')}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')})^{q-1} + \sum_a(\frac{\rho(s'',a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')})^q\] \[= -q\text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho(s'',a'')}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')}) - 1 + \sum_a(\frac{\rho(s'',a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho(s'',a')})^q\]- \(\text{ln}_q x + x^{q-1} = \frac{x^{q-1}-1}{q-1}+x^{q-1} = \frac{x^{q-1}-1 + (q-1)x^{q-1}}{q-1} = \frac{qx^{q-1}-1}{q-1}\) \(= \frac{qx^{q-1}-1 +q-q}{q-1} = q\frac{x^{q-1}-1}{q-1} +1 = q\text{ln}_qx +1\)
\(\mu^*(s)\)를 optiaml value인 \(V^*_q(s)\)라고 칭하고 싶다. 그래서 stationary condition에 \(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) = \rho^*(s,a)/\sum_{a'} \rho^*(s,a')\)를 곱한다. 그리고 a에 대해서 정리를 하면 아래처럼 정리된다.
\[0=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) - \mu^*(s)\] \[-q\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\text{ln}_q(\frac{\rho^*(s,a)}{\sum_{a'}\rho^*(s,a')}) -1+ \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \sum_{a''}(\frac{\rho^*(s,a'')}{\sum_{a'}\rho^*(s,a')})^q\] \[+ \sum\lambda^*(s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\] \[=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) - \mu^*(s)\] \[-q\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)) -1+ \sum_{a''}\pi_{\rho^*}(s,a)^q + \sum_a \lambda^*(s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\]KKT condition에 의해서 \(\lambda^*(s,a) =0\)
\[=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) - \mu^*(s)\] \[-q\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)) -1+ \sum_{a''}\pi_{\rho^*}(s,a)^q\] \[=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) - \mu^*(s)\] \[-q\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)) -1+ \sum_{a''}\pi_{\rho^*}(s,a)^q\]\(\sum_{s,a}x^q -1 = \sum_{s,a}(x^q-x) = \sum{s,a} (q-1) \frac{x^{q-1}-1}{q-1}x = (q-1)\sum_{s,a}x\text{ln}_qx\) 식을 이용
\[=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) - \mu^*(s)\] \[-q\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)) + (q-1)\sum_{s,a} \pi_{\rho^*}(s,a) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(s,a))\] \[=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) - \mu^*(s)\] \[-\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s))\]그러므로
\[\mu^*(s)=\sum_a\sum_{s'} r(s,a,s') P(s'|s,a)\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) + \gamma \sum_{s'} \mu^*(s') \sum_a P(s'|s,a) \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\] \[-\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s))\] \[=E_{s' \sim P,a \sim \pi}[r(s,a,s') + \alpha S_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(\cdot | s)) + \gamma\mu^*(s') |s]\]위 식은 Tsallis Bellman expectation(TBE)를 만족한다. 그러므로 \(\mu^*(s)\)를 $$V^{\pi_{\rho^*}}인 value of optimal policy라고 칭할 것이다. 물론 추가적인 증명이 필요하지만 이는 Theorem 10에서 증명을 할 것이다.
\(\mu^*=V^*_q\)라면 \(Q^*_q(s,a) = E_{s' \sim P}[r(s,a,s') + \gamma\mu^*(s')]\)를 얻을 수 있다.
\(\rho^*(s,a)/\sum_{a'}\rho^*(s,a')\) 를 \(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\)로 치환하고, \(Q^*_q(s,a) = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma \mu^*(s')]\), \(\mu^*(s) = V^*(s)\)라고 한다면 아래 식을 KKT condition을 이용하여 구할 수 있다.
\[Q^*_q(s,a) - V^*_q(s) - q\text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)) -1 + \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)^q = 0\] \[\frac{Q^*_q(s,a)}{q} - \frac{V^*_q(s) +1 - \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)^q}{q} = \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s))\] \[\text{exp}_q{\frac{Q^*_q(s,a)}{q} - \frac{V^*_q(s) +1 - \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)^q}{q}} =\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\]\(\sum_a\pi(a|s) =1\) 이므로 양변에 \(\sum\)을 넣는다.
\[\sum_a(\text{exp}_q{\frac{Q^*_q(s,a)}{q} - \frac{V^*_q(s) +1 - \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)^q}{q}}) =1\]이 식은 q-exponential distribution의 normalization equation이다. 그러므로 q-potential과 optimal value function과 관계를 얻을 수 있다.(식 24를 참고)
\[\psi_q(\frac{Q^*_q(s, \cdot)}{q}) = \frac{V^*_q(s) +1 - \sum_a(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s))^q}{q}\]결론적으로, optimal policy는 \(Q^*_q(s,\cdot)\) q-exponential distribution을 얻을 수 있다.
\[\text{exp}_q(\frac{Q^*_q(s,a)}{q} - \psi_q(\frac{Q^*_q(s,\cdot)}{q})) = \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\]이를 \(\mu^*\) 식에 대입하면 아래 식을 얻을 수 있다.
\[V^*_q(s) = \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \sum_{s'} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma V^*_q(s') P(s'|s,a)] - \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s))\] \[= \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) Q^*_q(s,a) - \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) \text{ln}_q(\pi_{\rho^*}(a|s))\] \[=\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s) Q^*_q(s,a) - \sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)(\frac{Q^*_q(s,a)}{q} - \psi_q(\frac{Q^*_q(s,\cdot)}{q}))\] \[=(q-1)\sum_a \pi_{\rho^*}(a|s)\frac{Q^*_q(s,a)}{q} + \psi_q(\frac{Q^*_q(s,\cdot)}{q})\] \[=\underset{a'}{q-\text{max}}(Q^*_q(s,a'))\]결론으로 아래의 Tsallis MDP의optimality condition를 얻을 수 있다.
\[Q^*_q(s,a) = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma V^*_q(s') |s,a]\] \[V^*_q(s) = \underset{a}{\text{q-max}} (Q^*_q(s,a))\] \[\pi^*_q(a|s) = \text{exp}_q (Q^*_q(s,a)/q - \psi_q(Q^*_q(s,\cdot)/q))\]5. Dynamic Programming for Tsallis MDPs
Tsallis policy tieration(TPI)와 Tsallis value iteration(TVI)라는 Tsallis MDP를 위한 dynamic programming algorithm을 소개한다. TPI는 policy evaluation과 improvement로 구성되어 있는 policy iteration method이다. fixed policy의 value function이 연산되고 난 후 policy가 value function에 의해 업데이트된다. TVI는 optimal value가 바로 업데이트되는 방식이다.
Tsallis Policy Iteration
Fixed plicy \(\pi\)를 이용하여 \(V^\pi_q\)와 \(Q^\pi_q\)를 연산한다. 원래 MDP와 비슷하게 Tsallis MDP는 expectation equation을 이용하여 연산할 수 있다.
\[Q^\pi_q(s,a) = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma V^\pi_q(s') |s,a]\] \[V^\pi_q(s) = E_{a \sim \pi}[Q^\pi_q(s,a) +\text{ln}_q(\pi(a|s))]\]위 식은 Tsallis Bellman Expectation(TBE)라고 칭한다.
Theorem 10
Tsallis Policy Evaluation
- Lemma 10.1
Proof.
\[V_{F+c1}(s) = E_{a \sim \pi} [F(s,a) + c - \text{ln}_q(\pi(a|s))] = E_{a \sim \pi}[F(s,a) - \text{ln}_q(\pi(a|s))]+c= V_F(s) + c\] \[[\Gamma^\pi_q(F+c1)](s,a) = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma V_{F+c1}(s')|s,a] = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') +\gamma V_F(s') + \gamma c |s,a]\] \[= E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma V_F(s') |s,a] + \gamma c = \Gamma^\pi_q F(s) + \gamma c\]- Lemma 10.2
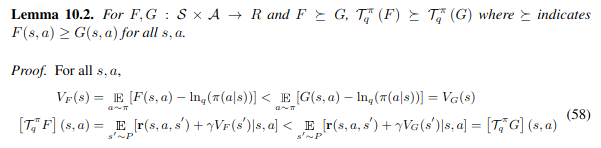
1
* 위 식의 부등호 방향이 맞는 지 의문이 있긴함.
- Lemma 10.3

Fixed policy \(\pi\)와 entropic index \(q \ge 1\), TBE operator \(\Gamma^\pi_q\)
Tsallis policy evaluation은 \(F_{k+1} = \Gamma^\pi_qF_k\)로 정의할 수 있다. 그러면 \(F_k\)가 converge하다면 TBE equation을 만족한다.
Proof of Tsallis Policy Evaluation
위의 lemma를 통해 \(\Gamma^\pi_q\)가 \(\gamma\)-contraction임을 증명하였고 Banach fixed point theorem에 의해 unique fixed point \(F_* = \Gamma^\pi_qF_*\)임을 얻을 수 있다. 그러므로 F에서부터 \(F_k\) sequence는 fixed point로 converge하다는 것을 얻을 수 있다. \(F_*\)가 unique이므로 \(F_*\)는 TBE equation을 만족하는 유일한 function이다. 그러므로 \(F_*=Q^\pi_q\)이다.
Theorem 11, 12
Tsallis Policy Improvement, Optimality of TPI
- Theorem 11: \(\pi_{k+1}\)을 updated policy라고 한다면 \(Q^{\pi_{k+1}}_q(s,a)\)는 \(Q^{\pi_k}_q(s,a)\)보다 더 크다.
Proof
\(\pi_{k+1}\)은 updated policy이고 policy를 최대화하는 것은 concave하므로 아래 식을 만족한다.
\[E_{a \sim \pi_{k+1}} [Q^{\pi_k}_q(s,a) - \text{ln}_q(\pi_{k+1}(a|s)) |s] \ge E_{a \sim \pi_{k}} [Q^{\pi_k}_q(s,a) - \text{ln}_q(\pi_{k}(a|s)) |s] = V^{\pi_k}_q(s)\] \[Q^{\pi_k}_q(s,a) = E_{s_1 \sim P}[r(s_0,a_0,s_1) + \gamma V^{\pi_k}_q(s_1) | s_0=s, a_0=a]\] \[\le E_{s_1 \sim P}[r(s_0,a_0,s_1) |s_0=s,a_0=a] + \gamma E_{s_1,a_1 \sim P, \pi_{k+1}}[Q^{\pi_k}_q(s_1,a_1) - \text{ln}_q(\pi_{k+1}(a_1|s_1))|s_0=s,a_0=a]\] \[= E_{s_1 \sim P} [r(s_0,a_0,s_1) | s_0=s,a_0=a] + \gamma E_{s_{1:2},a_1 \sim P, \pi_{k+1}}[r(s_1,a_1,s_2) - \text{ln}_q(\pi_{k+1}(a_1|s_1)) + \gamma V^{\pi_k}_q(s_2) | s_0=s, a_0=a]\] \[\le E_{s_1 \sim P}[r(s_0,a_0,s_1) + \gamma V^{\pi_{k+1}}_q(s_1) |s_0=s, a_0=a] = Q^{\pi_{k+1}}_q(s,a)\]- Theorem 12(Optimality of TPI): TPI converges into an optimal policy and value of a Tsallis MDP.
현재까지 TBE와 식의 Improvement를 증명하였다. 여기서는 TPI가 optimal policy와 Tsallis MDP value로 converge함을 증명하고자 한다.
Proof.
reward function r이 \(r_{\text{max}}\)의 uppder bound이고 \(Q^{\pi_k}_q\) 또한 한계가 있다. 그리고 \(Q^{\pi_k}_q\)는 monotonically non-decreasing(Theorem 11)이므로 어떤 \(\pi_*\)에 converge한다. \(Q^{\pi_k}_q\)의 unique한 solution은 \(\pi_*\)이고 Theorem 9에 의해 식들이 Optimal하므로 \(\pi_*=\pi^*_q\)가 되어 optimal solution이 된다.
Tsallis Value Iteration
Tsallis value iteration은 Tsallis policy evaluation과 동일한 방법으로 증명한다. Tsallis value iteration은 \(\Gamma j_q\)의 contraction property에 의해 converge하다. 그러므로 \(F_k\)는 fixed point \(\Gamma_q\)에 converge하다. 이 fixed point는 TBO equation을 만족한다.
Performance Error Bounds
TPI 혹은 TVI로부터 얻은 Tsallis MDP의 optimal policy의 error bound를 설명할 것이다. 이 error는 Tsallis entropy maximization에서 사용된 regularization term에 의해 발생한다. Tsallis MDP와 original MDP를 비교해서 error performance를 비교한다.
Theorem 14
Performance Error Bounds
- lemma 14.1
\([\Gamma F](s,a)\) \(\triangeq E_{s' \sim P}[r(s,a,s') + \gamma \underset{a'}{\text{max}}F(s',a') | s,a]\)
\[\Gamma^k_q F \succeq \Gamma^kF\]Proof. k=1이라면 Lemma 13.1에 의해 아래 식을 만족한다.
\([\Gamma F]\) \((s,a) = E_{s' \sim P} [r(s,a,s') + \gamma \underset{a'}{\text{max}}F(s',a') |s,a]\) \(\leq E_{s' \sim P}[r(s,a,s') + \gamma q-\underset{a'}{\text{max}}F(s',a') | s,a] =\) \([\Gamma_qF](s,a)\)
k=n이라면
\[\gamma^{n+1}F = \Gamma \Gamma^n F \preceq \Gamma_q\Gamma^nF \preceq \Gamma_q \Gamma^n_qF \preceq \Gamma^{n+1}_qF\]그러므로
\[V^* = \underset{t \to \infty}{\text{lim}} \Gamma^kF \preceq \underset{k \to \infty}{\text{lim}} \Gamma^k_q F = V^*_q\]Theorem 14.
Proof.
Upperbound는 original MDP가 \(J(\pi)\)를 최대화 하기 때문에 \(J(\pi^*_q) \leq J(\pi^*)\)가 된다.
Lower bound는 아래 식을 이용하여 증명된다.
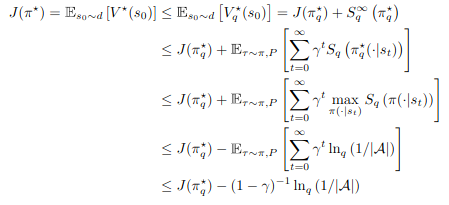
TPI와 TVI는 transition probability P를 가지고 value function을 update한다. 게다가 \(\psi_q\)를 연산하기 힘들다는 문제가 있다. 그래서 TPI를 actor-critic method로 확장하여 이 문제를 해결하고 large-scale model-free RL문제를 해결하고자 한다.
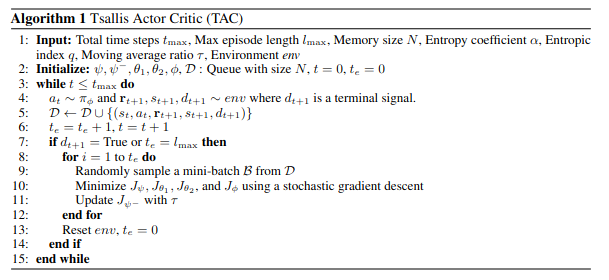
Tsallis Actor Critic for Model-Free RL
TAC에서는 5 가지 network를 사용한다. policy \(\pi_\phi\), state value \(V_\psi\), target value \(V_{\psi^-}\), 2 action values \(Q_{\theta_1}\), \(Q_{\theta_2}\)
policy를 update하는 것에 \(\pi_\phi\)가 필요하지만 intractable하기 때문에 stochastic gradient를 사용한다. 그리고 reparameterization을 이용하여 approximation한다.
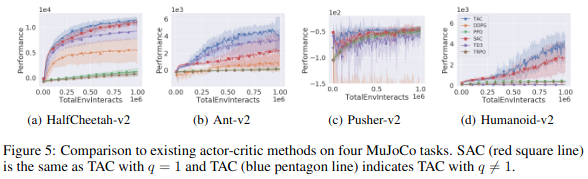
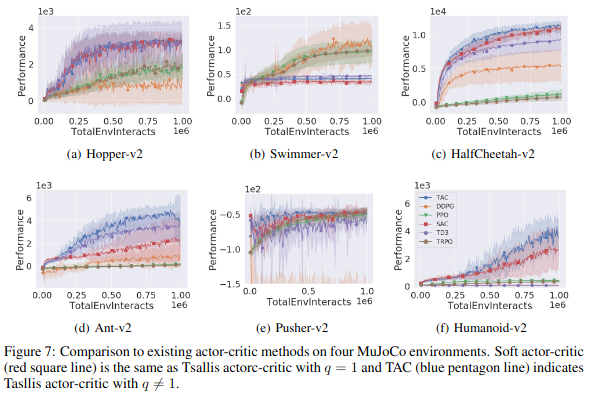
Experiment
이 논문에서는 MuJoCo를 이용하여 다른 논문과 비교를 하였다. 우선 entropic index가 TAC에 어떤 영향을 미치는 지 실험을 하였다.
q value를 {0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.2, 1.5, 1.7, 2.0, 3.0, 5.0}으로 변경하며 실험하였다. entropy coefficient \(\alpha\)는 0.05(Humanoid-v2), 0.2(otheres)로 고정하였다.
실험 결과 \(1 \le q <2\) 일경우 가장 좋은 결과를 보여주었다. \(0 < q <1\)일 경우 별로인 결과를 보여주었다. SG entropy보다 더 exploitation을 방해하기 때문이다.
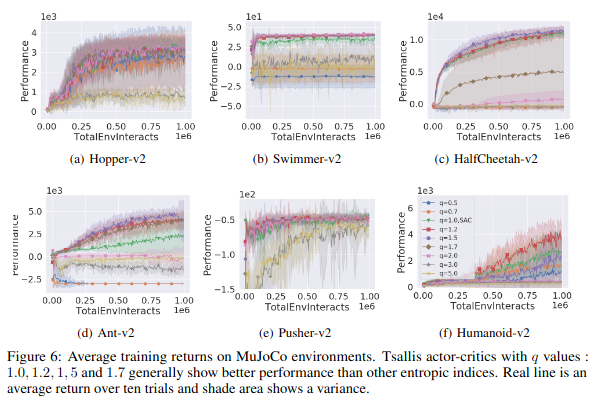
다른 논문과 비교시 TAC를 제외하고 SAC가 가장 좋은 결과를 보여주었고 TAC는 SAC보다 짧은 episode안에 좋은 결과를 보여주는 것을 확인할 수 있다.