목차
Problem definition
Agent의 적절한 action을 위해서 centralised action-value function인 \(Q_{tot}\)이 필요하다. 하지만 많은 agent가 있거나 만약에 \(Q_{tot}\) 얻더라도 이를 다시 각각의 agent에 사용하기 위해 각각의 observation을 기반으로한 행동을 얻을 수 있는 decentralised policy를 얻기가 힘들다.
Related work
- IQL
- 각각의 agent가 actor-critic을 사용하는 방법이다.
- Converge하는 것이 보장되지 않으며 학습 성능이 그때그때 다르다는 문제가 있다.
- COMA
- Centralised learning 방식이다.
- On-policy 방식이여서 sample을 다시 사용할 수 없으며 agent가 늘어날 수록 비효율적이라고한다.
- VDN
- 각각의 \(Q_a\)를 더하여 \(Q_{tot}\)를 만드는 방법이다.
- Greedy하게 \(Q_a\)를 고르면 \(Q_{tot}\)도 성능이 올라갈 것이라는 논문
- 몇몇 state 정보를 사용하지 않아 Centralised action-value function의 학습에 지장이 있다.
QMIX
VDN의 full factorisation 방식을 사용하는 대신 argmax를 이용한다.
global argmax \(Q_{tot}\)가 각각의 \(Q_a\)에 argmax한 결과가 동일하다는 것을 증명해야한다. 이 방식은 off-policy 방식이 된다.
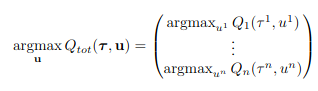
VDN은 위 공식을 만족하는 것을 증명하였다. 하지만 Qmix는 observation을 기반으로하기 때문에 위 공식은 monotonic function으로 일반화가 가능하다.
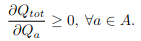
- Agent network
- 각 agent는 한 개의 agent network \(Q_a(\tau^a, u^a)\)를 가진다.
- Monotonic function의 제약식을 만족하기 위해서 network의 weight를 non-negative하도록 설정한다.
- Mixing network
- \(Q_{tot}\)를 위한 network로 여러 hypernetwork들의 network weight를 이용하여 만들어진다.
- 각 hypernetwork는 state s 를 input으로 받으며 output은 mixing network의 weight로 사용된다.
- Single linear layer로 구성되어 있으며 absolute activation function을 사용한다.
- Mixing network의 마지막 두 Single linear layer는 Relu activation을 사용한다.
- State 정보를 바로 mixing network에서 사용하는 것이 아닌 hypernetwork를 사용하는 이유는 extra state information을 non-monotonic 방법으로 사용할 수 있기 때문이라고한다.
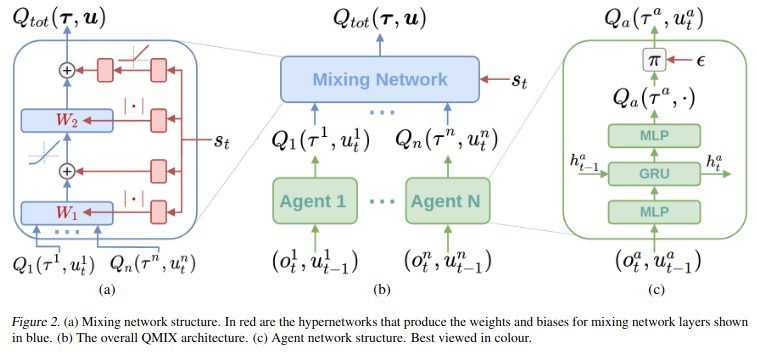 Qmix 구조
Qmix 구조
이렇게 만들어진 \(Q_{tot}\)는 아래 식을 이용해서 update된다.
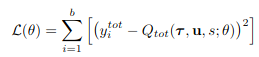
Representational Complexity
Qmix는 \(Q_{tot}\)가 각각의 action-value function이 non-linear monotonic function 조합으로 표현될 수 있다고 하였다. 이는 VDN의 linear monotonic function으로 확장이 될 수 있지만 \(Q_{tot}\)와 \(Q_a\)의 관계를 monotonicity를 이용해 제약을 걸어 확장에 제약을 걸었다.(mixing network 사용)
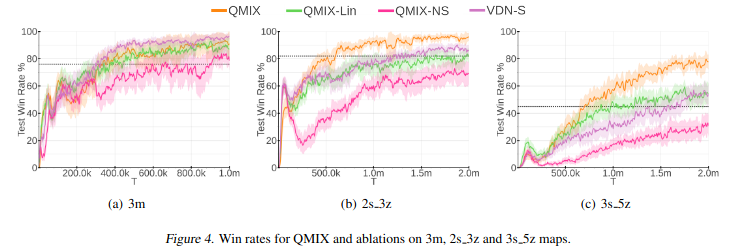
뒤쪽 representational complexity 실험과 VDN과 비교한 실험에서 representational complexity로 인해 VDN보다 좋은 결과를 얻을 수 있다고 말을 하고 있으며 non-monotonic problem에 대해서 완벽히 cover가 안된다는 것 또한 보여준다.
Experiment
기존 알고리즘(IQL, VDN) 대비 좋은 결과를 가지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
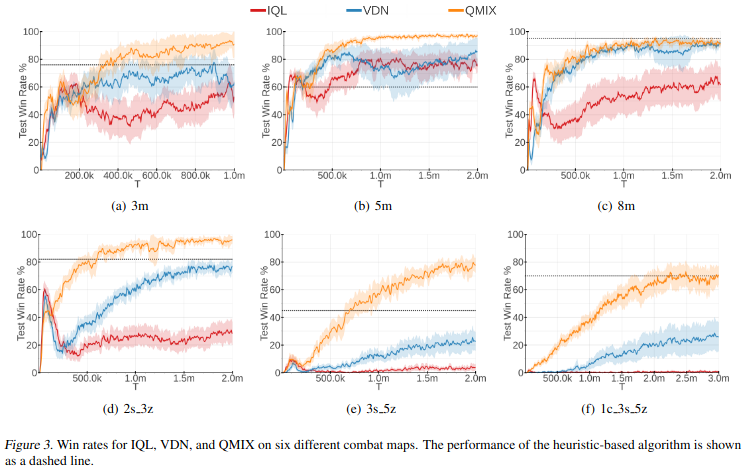
Qmix의 non-linear monotonic function의 장점을 보여주는 실험이다. 간단한 3m의 case 경우 높은 승률을 보여주지만 여러 종류의 agent가 섞일 경우 Qmix가 가장 좋은 결과를 보여준다.
Review comment
Idea 자체는 간단할 수 있지만 전체적으로 이해하기에는 디테일하게 봐야할 부분이 많았던 논문이 였던 것같다. 또한 VDN 논문을 먼저 보는 것이 더 좋았을 것같다. 또한 monotonic 증명에 관한 논문이 reference로 들어가 있는 데 논문의 아이디어 스케치를 이해하기 위해서는 이 논문도 리뷰를 해야할 것같다. 또한 COMA에 대한 비교군이 없는 게 아쉽다.
Reference
- Tan, Ming. “Multi-agent reinforcement learning: Independent vs. cooperative agents.” Proceedings of the tenth international conference on machine learning. 1993.
- Foerster, Jakob, et al. “Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients.” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vol. 32. No. 1. 2018.
- Rashid, Tabish, et al. “Qmix: Monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning.” International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2018.