목차
- Problem definition
- Background
- Multi-Actor-Attention-Critic(MAAC)
- Algorithm
- Experiment
- Review comment
- Reference
Problem definition
이전 Multi-agent Reinforcement learning을 위해서 하는 가장 간단한 방법은 독립적인 agent를 두고 학습하는 방법이지만 이 방법은 환경이 stationary하고 markovian이여야하는 가정을 위반한다. 그래서 다른 방법으로 모든 agent로부터 정보를 얻는 centrally critic을 두는 방법이다. 하지만 이 알고리즘은 여러 agent를 학습하고 다루기에 어렵다는 문제가 있다. 그래서 이 논문은 attention mechanism을 이용하여 centralized critic을 학습하는 방법을 제안한다. 이 방법으로 인하여 각 agent는 특정 다른 agent의 정보에 집중하여 정보를 얻어 학습할 수 있게 된다.
Background
Attention models
이 논문에서는 attention models을 이용하여 critic을 만드는 방법을 제안한다. 이전에 Seq2Seq 구조에서 많이 사용하던 방법이다. 논문에 부족하던 background를 간단히 설명하기 위해서 Attention model의 기초가 되는 방법부터 설명을 하겠다.
간단한 예제로 기초 방법을 설명하겠다. 해당 내용은 video를 참고하여 만들었다.
Key, query, value 세 가지 파라미터가 있다. Query의 input을 받았을 때 key값과 유사도를 계산한다. 이후 유사도와 value 값을 곱하여 output을 만든다. 즉 유사도를 이용하여 해당 value의 어떤 값에 집중(attention)을 해야하는 지 계산한다.
example)
Query: ‘유재석’
dictionary(key:value): {‘유재석’: ‘지미유’, ‘이효리’: ‘천옥’, ‘엄정화’: ‘만옥’}
Query로 ‘유재석’이 들어 왔을 때 dictionary를 이용하여 유사도를 판단한다. 유사도는 {1,0,0}이 나올 것이고 이 유사도를 dictionary의 value와 곱하면 output으로 지미유가 나온다. 아래는 해당 과정을 코드로 나타낸 것이다.
- Similarity(query, key): key와 query 유사도(sim) 계산
1 2 3 4 5
def Similarity(query, key): if query == key: return 1 else: return 0
- SimXValue(sim, value): 유사도와 value를 곱한다.
1 2 3
def SimXValue(sim, value): output = sim * int(value) return output
- Result: 유사도와 value를 곱한 값의 합을 return
\(\text{result} = \underset{i}{\sum} \text{similarity(key,query)} * \text{value}\)1 2
def Result(outputs): return sum(outputs)
위 방법은 dictionary 형태로 attention model은 위와 비슷한 방법이다. 우선 query와 key의 유사도를 계산한 후 value의 가중합을 계산한다. 아래 식은 attention model의 수식을 나타낸다.
\[A(q,k,v) = \underset{i}{\sum} \text{softmax}(f(k,q))v\]위에서 f는 similarity function으로 dot product나 scaled dot product 등을 이용한다.
Dot product
Attention score(similarity) = \(\sum Q_i * K_i\)
Scaled dot product
Attention score(similarity) = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}}\sum Q_i * K_i\)
더 자세한 설명은 이 video를 참고하여 이해하면 될 것같다. 이전에도 attention model을 이용한 Multi-agent 논문이 있었지만 이 논문은 policy사이의 공유 정보에 초점을 두었기 때문에 더 좋은 성능 보여준다고 말한다.
Soft Actor-Critic
Soft Actor-Critic(SAC)는 Policy gradient 방법의 대표적으로 좋은 성능을 보여주는 논문으로 policy graident에 entropy 개념을 도입하여 방법이다. Entropy를 이용하여 exploration을 더 잘할 수 있도록 하였다. 이 논문의 key idea와 구조만을 본다고 한다면 안 읽어도 될 것 같다.
SAC의 policy gradient 공식은 아래와 같다.
\(L_Q(\psi) = E_{(s,a,r,s') \sim D} [(Q_{\psi}(s,a) - y)^2]\)
where, \(y = r(s,a) + \gamma E_{a' \sim \pi(s')}[Q_{\bar{\psi}}(s',a')]\)
\(\nabla_{\theta} J(\pi_{\theta}) = E_{s \sim D, a \sim \pi}[\nabla_{\theta} log(\pi_{\theta}(a \vert s)) (-\alpha log(\pi_{\theta}(a \vert s)) + Q_{\psi}(s,a) - b(s)]\)
where b(s) is a state-depedent baseline(V)
Multi-Actor-Attention-Critic(MAAC)
Notion
- j: the set of all agents except i as \i
- \(Q_i^{\psi}(o,a)\): agent i의 observation과 action와 다른 agent의 정보를 이용하며 만든 함수
where \(f_i\) is a 2-layer multi-layer perceptron(MLP), \(g_i\) 1-layer MLP
- \(x_i\): contribution from toher agents
where \(v_j\) is a function of agent j’s embedding, encoded with an embedding function and then linearly transformed by a shared matrix V, h is leaky ReLU.
- Attention score(\(\alpha_j\))
MAAC의 critic 구조는 아래 그림과 같다. observation과 action을 이용하여 e를 만든다.(특징 추출) \(e_i\)와 \(e_j\)를 query와 key로 유사도를 측정을 하고 value와 곱하여 contribution을 계산한다. 이를 이용하여 agent i가 어떤 agent의 정보를 얼마나 이용해야하는 지 계산하게 된다. 이 값들은 학습을 통하여 설정된다.
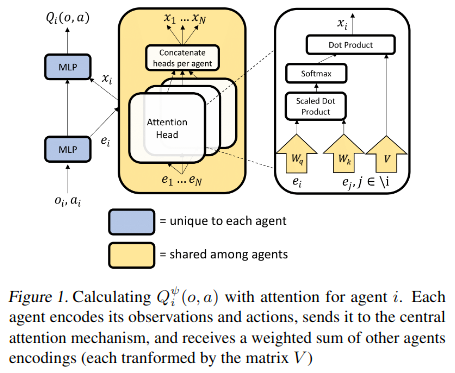 MAAC Architecture
MAAC Architecture
Actor와 Critic의 update는 위의 SAC 공식을 이용하여 update하게 된다.
\(L_Q(\psi) = E_{(s,a,r,s') \sim D} [(Q_{\psi}(s,a) - y)^2]\)
where, \(y = r(s,a) + \gamma E_{a' \sim \pi(s')}[Q_{\bar{\psi}}(s',a')]\)
\(\nabla_{\theta} J(\pi_{\theta}) = E_{s \sim D, a \sim \pi}[\nabla_{\theta} log(\pi_{\theta}(a \vert s)) (-\alpha log(\pi_{\theta}(a \vert s)) + Q_{\psi}(s,a) - b(s)]\)
where b(s) is a state-depedent baseline(V)
b(s)는 아래와 같은 공식으로 표현된다.
\[b(o,a_{\backslash i}) = E_{a_i \sim \pi_i(o_i)}[Q_i^\psi(o,(a_i,a_{\backslash i}))] = \underset{a'_i \in A_i}{\sum} \pi(a'_i \vert o_i) Q_i(o, (a'_i, a_{\backslash i}))\]\(Q_i\)에서 agent i의 action을 제거하고 모든 action의 value를 사용하였다. 그리고 위 공식을 사용하기 위해 \(e_i=g_i(o_i,a_i)\) 대신 \(e_i=g^o_i(o_i)\)를 사용하였다.
Algorithm
MAAC의 알고리즘은 아래와 같다.
 MAAC Algorithm
MAAC Algorithm
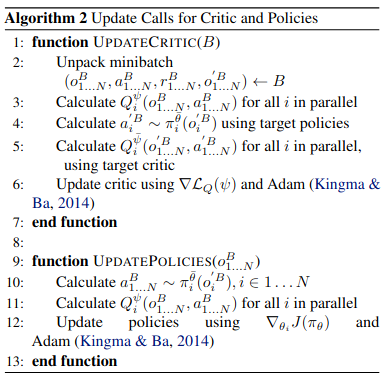 Update Actor Critic
Update Actor Critic
Experiment
이 논문에서는 실험 결과를 입증하기 위해 이전과 같은 starcraft2 환경이 아닌 다른 두 환경을 이용하였다. 첫 번째는 Cooperative Treausre Collection(CTC)이라는 환경으로 6 개의 treasure hunter와 2 개의 treasure bank(총 8개의 agent)로 이루어져 잇으며 treasure hunter는 treasure를 모으고 treasure bank에 treasure를 내보낸다. 두 번째는 Rover-Tower로 한 pair로 이루어진 rover와 tower가 있고 rover는 tower의 정보만을 이용하여 goal을 목표로 이동한다. tower는 탐사 로봇을 포함하여 목적지를 찾을 수 있고 paired 된 탐사 로봇에게 5개의 메시지(상,하,좌,우,정지?) 중 하나를 보낼 수 있다.
아래는 다른 multi-agent 방법과 비교한 결과이다. MAAC(uniform)은 attention score를 동일한 비율(uniform, 1/N)으로 한 결과를 의미한다. MAAC는 두 환경 모두 좋은 결과를 보여주고 Rover-tower의 경우 MAAC(uniform)이 성능이 급격히 하락하는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 Rover-tower 실험이 attention model가 어떤 효과를 보여주는 지 입증하는 실험이라는 것을 알 수 있게 해준다. COMA 논문은 비슷한 action space를 가지는 경우에는 좋은 결과를 보여주는 것을 확인할 수 있었고 MADDPG의 경우 agent에 따라 큰 observation space를 가져야하기 때문에 CTC 환경에서 좋지 않은 결과를 보여주는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
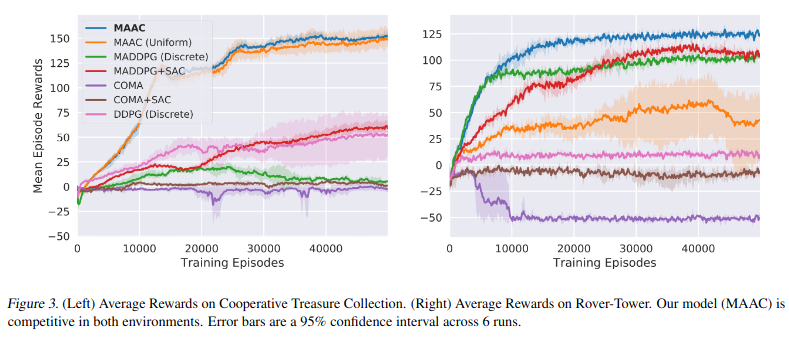 Performance comparing with others
Performance comparing with others
MADDPG와 agent가 증가함에 따른 실험 결과를 비교하면 MAAC는 비슷한 성능을 보여주지만 MADDPG는 증가함에 따라 성능이 낮아지는 것을 아래 그림에서 확인할 수 있다.
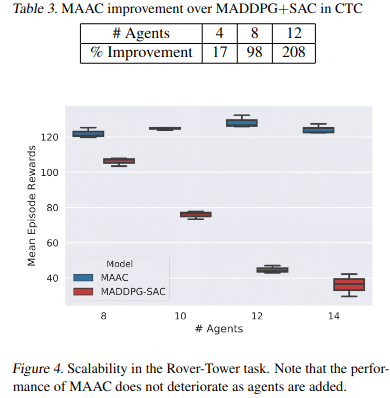 Scalability in the Rover-Tower task
Scalability in the Rover-Tower task
Rover Tower의 경우 tower의 어떤 정보에 attention 해야하는 지가 중요하게 작용하는 부분이 있다. 아래 그림은 tower 3와 pairing된 rover 1이 어느 tower에 attention을 하고 있는 지 attention score를 보여주는 그림이고 pairing된 tower3에 가장 높은 attetnion score를 가지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
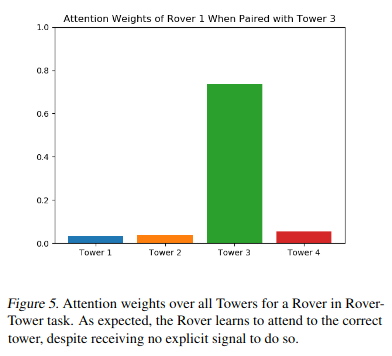 Attention weights over all Towers
Attention weights over all Towers
Review comment
이전 posting의 논문들인 LIIR이나 QMIX 논문과 비교 내용이 없다는 것이 아쉽다. Attention 알고리즘이 가지는 의미와 효과를 실험적으로 잘 보여준 것같고 범용적인 multi-agent 환경에서 좋게 쓰일 수 있는 지에대해서는 추가적인 실험과 LIIR, QMIX 논문과 비교를 하는 것이 좋을 것같다. Attention 알고리즘을 적용하였다는 새로운 아이디어를 적용했다는 것에 큰 의미를 가지는 것같다. 이전 논문과 다르게 다른 agent의 정보를 이용하기 때문에 더 좋은 결과를 보여주는 것 같다.
Reference
- Iqbal, Shariq, and Fei Sha. “Actor-attention-critic for multi-agent reinforcement learning.” International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019.
- Vaswani, Ashish, et al. “Attention is all you need.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03762 (2017).
- DMQA Open Seminar; Graph Attention Networks
- Haarnoja, Tuomas, et al. “Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor.” International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2018.